Index
- Part 1: Exploring Multi-Threading in C++
- Part 2: Exploring Multi-Threading in C++ Cont.
- Part 3: Exploring Multi-Threading in C++: Loading Textures
- Part 4: Exploring Multi-Threading in C++: Parallelizing Ray Tracing
Specific Worker Threads for Specific Jobs
My next test case is to have different worker thread to run different kinds of tasks. The idea is to have a couple of threads for important jobs, others for less important jobs. I’ve split the tasks into different Job queues for simplicity.
static std::mutex g_mutexLowJobQ;
static std::mutex g_mutexMediumJobQ;
static std::mutex g_mutexHighJobQ;
std::queue<CalcPiJob*> GetJobsOfType(int count, int iterations)
{
std::queue<CalcPiJob*> jobQ;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i)
{
jobQ.emplace(new CalcPiJob(iterations));
}
return jobQ;
}
void RunThreadedPriority()
{
int nHighThreads = 3;
int nMediumThreads = 2;
int nLowThreads = 2;
std::queue<CalcPiJob*> lowJobQ = GetJobsOfType(Settings::JobCountLow, Settings::IterationCountLow);
std::queue<CalcPiJob*> mediumJobQ = GetJobsOfType(Settings::JobCountMedium, Settings::IterationCountMedium);
std::queue<CalcPiJob*> highJobQ = GetJobsOfType(Settings::JobCountHigh, Settings::IterationCountHigh);
std::vector<std::thread> threads;
std::atomic<bool> hasHighJobsLeft = true;
for (int i = 0; i < nHighThreads; ++i)
{
std::thread t([&]() {
ExecuteJobsQ(hasHighJobsLeft, highJobQ, g_mutexHighJobQ);
});
threads.push_back(std::move(t));
}
std::atomic<bool> hasMediumJobsLeft = true;
for (int i = 0; i < nMediumThreads; ++i)
{
std::thread t([&]() {
ExecuteJobsQ(hasMediumJobsLeft, mediumJobQ, g_mutexMediumJobQ);
});
threads.push_back(std::move(t));
}
std::atomic<bool> hasLowJobsLeft = true;
for (int i = 0; i < nLowThreads; ++i)
{
std::thread t([&]() {
ExecuteJobsQ(hasLowJobsLeft, lowJobQ, g_mutexLowJobQ);
});
threads.push_back(std::move(t));
}
// main thread
while (hasHighJobsLeft || hasMediumJobsLeft || hasLowJobsLeft)
{
if (hasHighJobsLeft)
{
ExecuteJobsQ(hasHighJobsLeft, highJobQ, g_mutexHighJobQ);
}
else
{
// wait for other threads to complete.
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(10));
}
}
const int threadCount = threads.size();
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; ++i)
{
threads[i].join();
}
}
Run time with 8 threads: 6059 ms. ( 4 High Job threads, 2 medium and 2 low threads. )
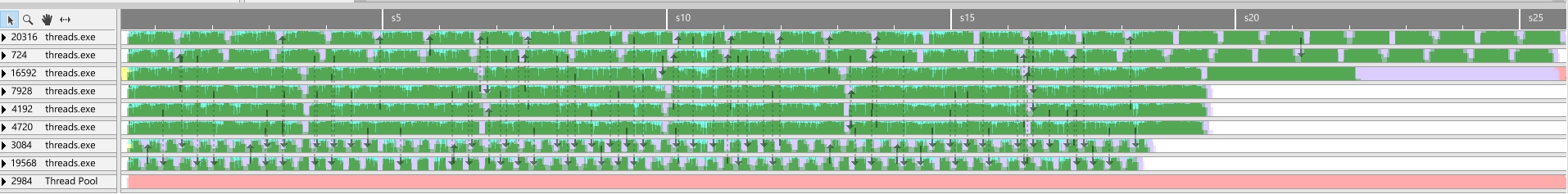
The profile image show the 4 threads handling only big jobs, 2 threads handling medium jobs and the other 2 threads handling smaller jobs. As we can see, this won’t win us much time, since when some thread finish their work, they stand idle, not contributing to the bigger picture.
We can try to fix that by implementing some kind of work stealing. When a thread has no more jobs meant for them, they can steal jobs from other thread queues.
Specific Threads with Work Stealing
This next test is just that. Each thread type was setup to grab a job of less priority from their main one, once they run out of jobs. Hopefully we will prevent threads from going idle.
void RunThreadedPriorityWorkStealing()
{
int nHighThreads = 5;
int nMediumThreads = 1;
int nLowThreads = 1;
std::queue<CalcPiJob*> lowJobQ = GetJobsOfType(Settings::JobCountLow, Settings::IterationCountLow);
std::queue<CalcPiJob*> mediumJobQ = GetJobsOfType(Settings::JobCountMedium, Settings::IterationCountMedium);
std::queue<CalcPiJob*> highJobQ = GetJobsOfType(Settings::JobCountHigh, Settings::IterationCountHigh);
std::vector<std::thread> threads;
std::atomic<bool> isHighPriorityThreadsActive = true;
for (int i = 0; i < nHighThreads; ++i)
{
std::thread t([&]() {
while (isHighPriorityThreadsActive)
{
CalcPiJob* currentJob = GetAndPopJob(highJobQ, g_mutexHighJobQ);
// if no more High Jobs, take on Medium ones.
if (!currentJob)
{
currentJob = GetAndPopJob(mediumJobQ, g_mutexMediumJobQ);
}
// if no more Medium Jobs, take on Small ones.
if (!currentJob)
{
currentJob = GetAndPopJob(lowJobQ, g_mutexLowJobQ);
}
if (currentJob)
{
currentJob->DoWork();
delete currentJob;
}
else
{
isHighPriorityThreadsActive = false;
}
}
});
threads.push_back(std::move(t));
}
std::atomic<bool> isMediumThreadsActive = true;
for (int i = 0; i < nMediumThreads; ++i)
{
std::thread t([&]() {
while (isMediumThreadsActive)
{
CalcPiJob* currentJob = GetAndPopJob(mediumJobQ, g_mutexMediumJobQ);
// if no more Medium Jobs, take on Small ones.
if (!currentJob)
{
currentJob = GetAndPopJob(lowJobQ, g_mutexLowJobQ);
}
if (currentJob)
{
currentJob->DoWork();
delete currentJob;
}
else
{
isMediumThreadsActive = false;
}
}
});
threads.push_back(std::move(t));
}
std::atomic<bool> isLowThreadsActive = true;
for (int i = 0; i < nLowThreads; ++i)
{
std::thread t([&]() {
while (isLowThreadsActive)
{
CalcPiJob* currentJob = GetAndPopJob(lowJobQ, g_mutexLowJobQ);
if (currentJob)
{
currentJob->DoWork();
delete currentJob;
}
else
{
isLowThreadsActive = false;
}
}
});
threads.push_back(std::move(t));
}
// main thread
while (isLowThreadsActive || isMediumThreadsActive || isHighPriorityThreadsActive)
{
if (isHighPriorityThreadsActive)
{
CalcPiJob* currentJob = GetAndPopJob(highJobQ, g_mutexHighJobQ);
// if no more High Jobs, take on Medium ones.
if (!currentJob)
{
currentJob = GetAndPopJob(mediumJobQ, g_mutexMediumJobQ);
}
// if no more Medium Jobs, take on Small ones.
if (!currentJob)
{
currentJob = GetAndPopJob(lowJobQ, g_mutexLowJobQ);
}
if (currentJob)
{
currentJob->DoWork();
delete currentJob;
}
else
{
isHighPriorityThreadsActive = false;
}
}
else
{
// wait for other threads to complete.
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(10));
}
}
const int threadCount = threads.size();
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; ++i)
{
threads[i].join();
}
}
Run time with 8 threads: 2625 ms.
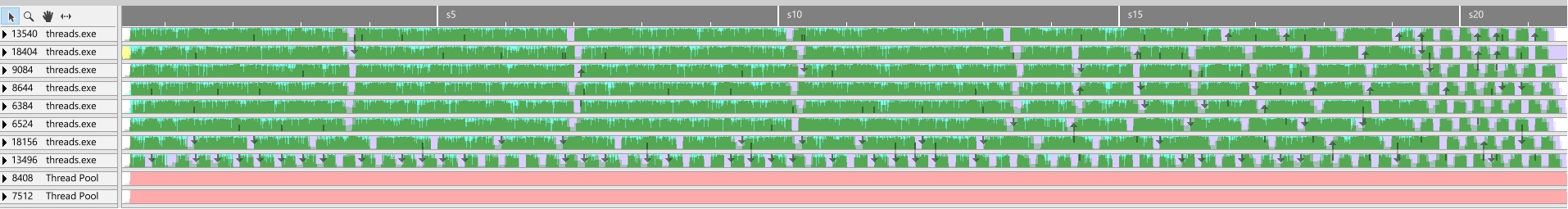
Now we can see that the high priority worker threads started to take on medium sized jobs as soon as the higher ones depleted, and then the small jobs followed.
Synchronizing Threads
Now lets say I’m processing data and I need to start Jobs in sync in between multiple threads, or maybe I’m building a game engine and my main update loop needs to start at the same time as the physics loop in some other thread. Whichever the case, I tough looking up synchronization mechanisms was worth doing as well.
std::mutex g_syncMutex;
std::condition_variable g_conditionVariable;
void RunSynchronizedThreads()
{
int nThreads = std::thread::hardware_concurrency() - 1;
std::vector<std::thread> threads;
std::queue<CalcPiJob*> jobQ = GetJobsQ();
std::atomic<bool> signal = false;
std::atomic<bool> threadsActive = true;
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; ++i)
{
std::thread t([&]() {
while (threadsActive)
{
// Tell main thread, worker is available for work
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(g_syncMutex);
g_conditionVariable.wait(lk, [&] { return signal == true; });
}
CalcPiJob* currentJob = GetAndPopJob(jobQ, g_mutexJobQ);
if (currentJob)
{
currentJob->DoWork();
delete currentJob;
}
else
{
threadsActive = false;
}
}
});
threads.push_back(std::move(t));
}
// main thread
std::atomic<bool> mainThreadActive = true;
while (mainThreadActive && threadsActive)
{
// send signal to worker threads, they can start work.
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(g_syncMutex);
signal = true;
}
g_conditionVariable.notify_all();
// send signal to worker threads, so they have to wait for their next update.
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lk(g_syncMutex);
signal = false;
}
g_conditionVariable.notify_all();
// main thread work.
CalcPiJob* currentJob = GetAndPopJob(jobQ, g_mutexJobQ);
if (currentJob)
{
currentJob->DoWork();
delete currentJob;
}
else
{
mainThreadActive = false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; ++i)
{
threads[i].join();
}
}
Run time: 2674 ms
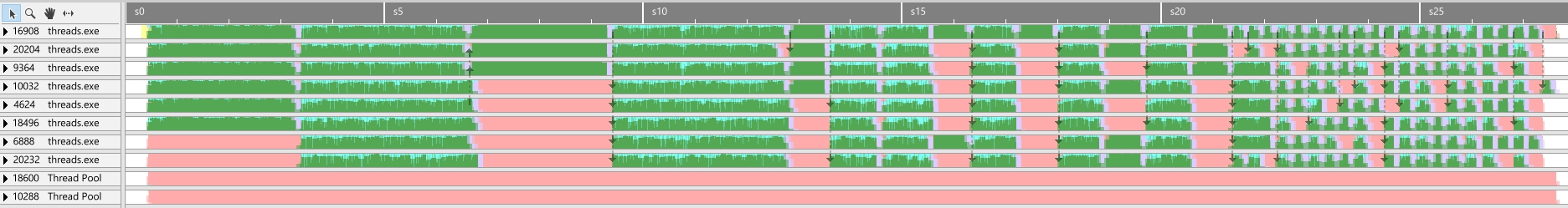
I’ve setup this one up so worker thread only start at the same frequency of the main thread. The goal here was to use condition variables to synchronize the threads, and hopefully confirm it with the profiler., which we can look at in the image above.
| Test Run | Time | Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Single Thread + One Worker Thread | 10396 | 1.99x |
| MT | 2625 | 7.88x |
| MT w/ Priority | 6059 | 3.4x |
| MT w/ Work Stealing | 2625 | 7.8x |
| Synchronized Threads | 2674 | 7.7x |